


Neurofeedback
The scientific basis of the methodOur brain, the most complex and powerful computing system on the planet, governs all aspects of our being, including our personality, temperament, emotions, and executive functions.
Various methods, such as solving crosswords, navigating mazes, tackling puzzles, and learning new languages and skills, indirectly enhance brain function. But what if we could directly train the areas of the brain that are "weaker"?
Neurofeedback is a method that allows for direct brain training. It is a type of biofeedback that uses feedback on the brain's electrical activity to normalize and optimize cognitive and emotional processes.

EEG
The basic tool for neurofeedbackThe basic tool for neurofeedback is the electroencephalogram (EEG). This non-invasive brain imaging technique allows for real-time monitoring of mental states through brain waves.
Neurofeedback is a type of biofeedback method that uses feedback on the brain's electrical activity to normalize and optimize cognitive and emotional processes. Essentially, it is applied neuroscience. The term EEG biofeedback is also used to specify the type of feedback being provided. Neurofeedback is a method that has emerged from scientific laboratories and research, and it is fully based on scientific principles.
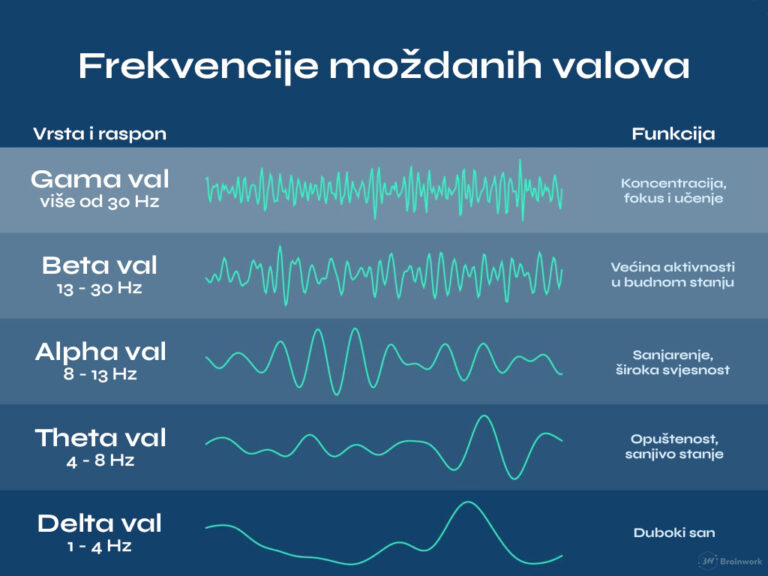
In neuroscience, we differentiate five basic types of brain waves:
- check_circledelta
- check_circletheta
- check_circlealpha
- check_circlebeta
- check_circlegamma
Delta waves (1 - 4 Hz) in a waking state are associated with learning difficulties and brain damage. Theta waves (4 - 8 Hz) indicate drowsiness, reduced levels of arousal, disengagement, and internal focus, as well as visualization and creativity.
Alpha waves (8 - 12 Hz) in a waking state are linked to daydreaming, internal orientation, and an awake state with broad awareness.
In neurofeedback, beta waves are divided into three categories: sensory-motor rhythm (SMR), mid-range beta, and high beta. Each of these waves is associated with specific mental states. The sensory-motor rhythm (12 - 15 Hz) is connected to reduced motor and sensory activity, as well as calm focus and insight. Mid-range beta waves (15 - 20 Hz) are linked to attention, cognitive activity, and problem-solving. High beta waves (20 - 35 Hz) are associated with mental tension, rumination, and anxiety. Gamma waves (35 - 42 Hz) are connected to cognitive flexibility and heightened concentration.

01
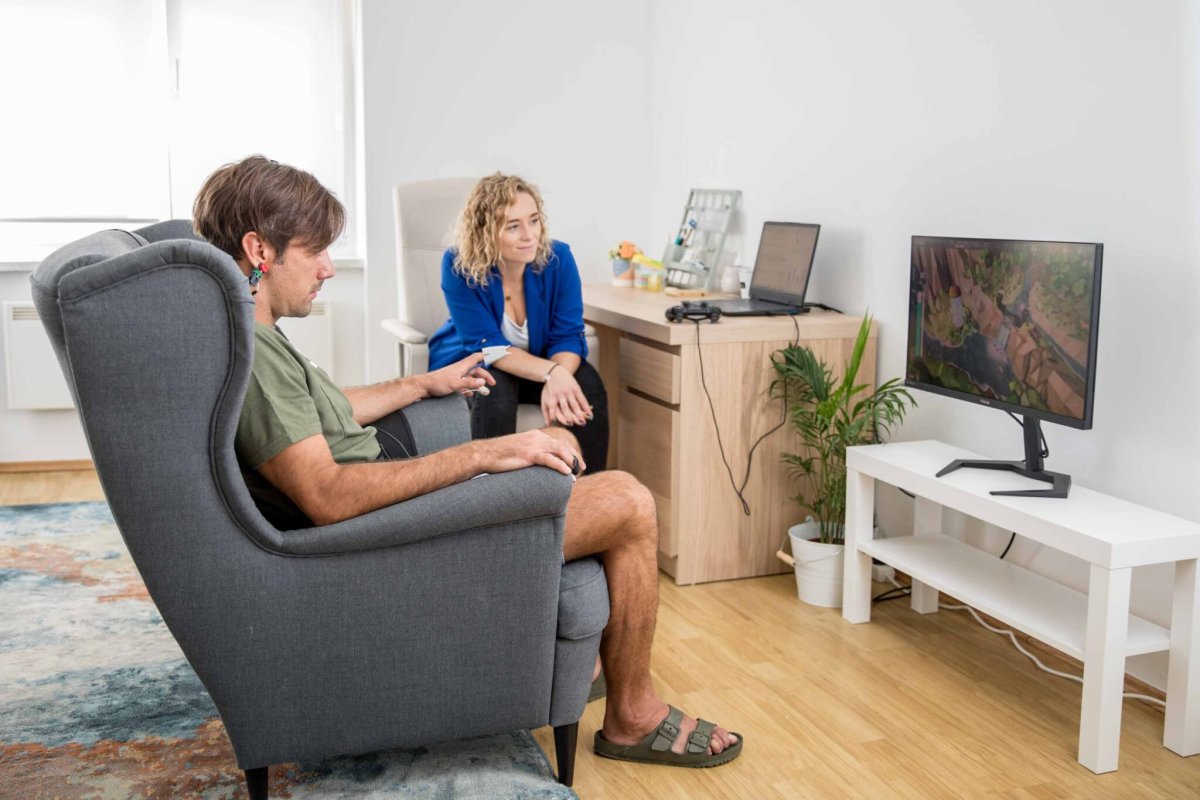
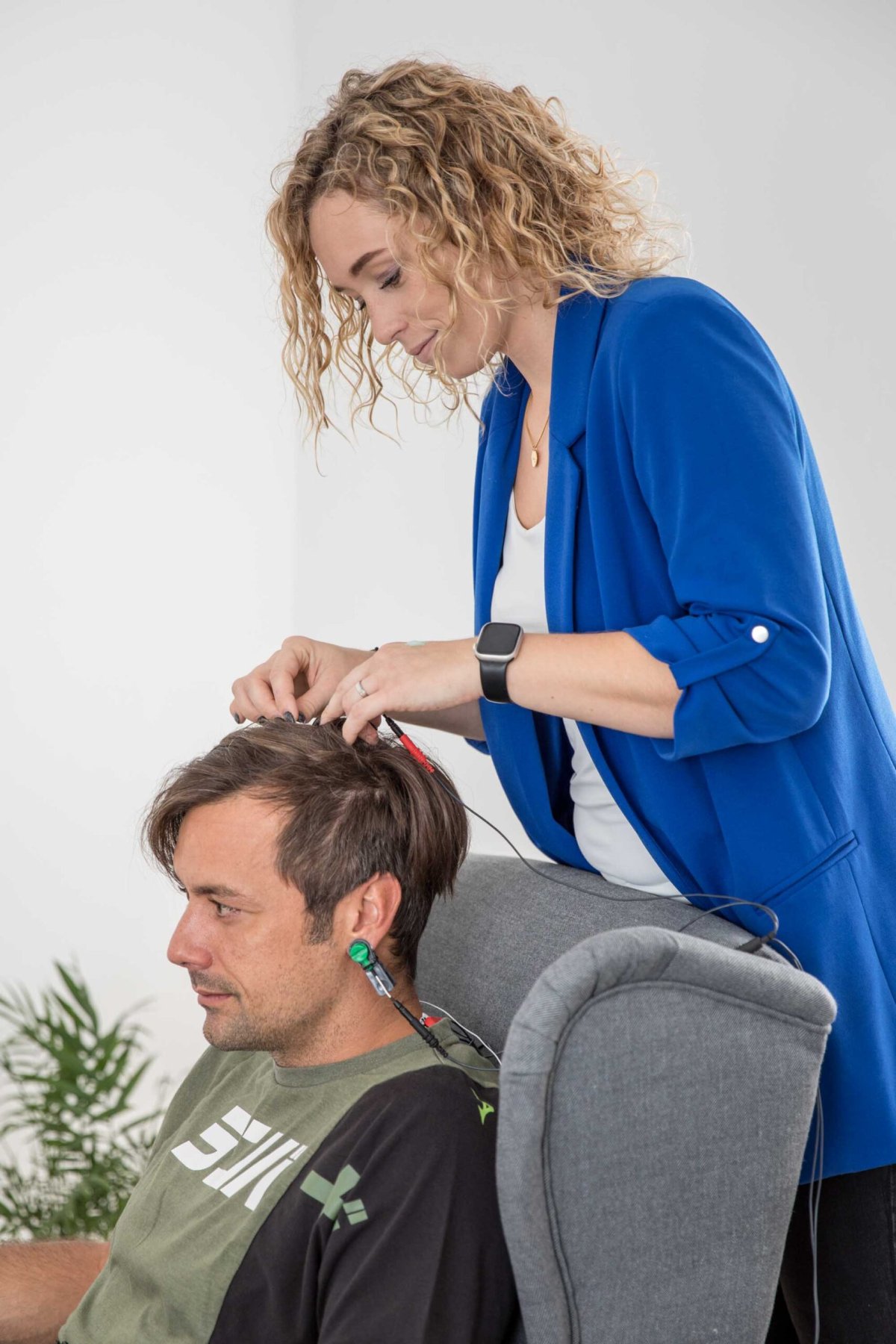
At the beginning of the training, the individual fills out a brief questionnaire about their daily routines and relaxes in a comfortable chair. Sensors are placed on the ears and head—three electrodes that collect brain activity. Then, a training plan is created and goals are set. After that, the actual training begins.
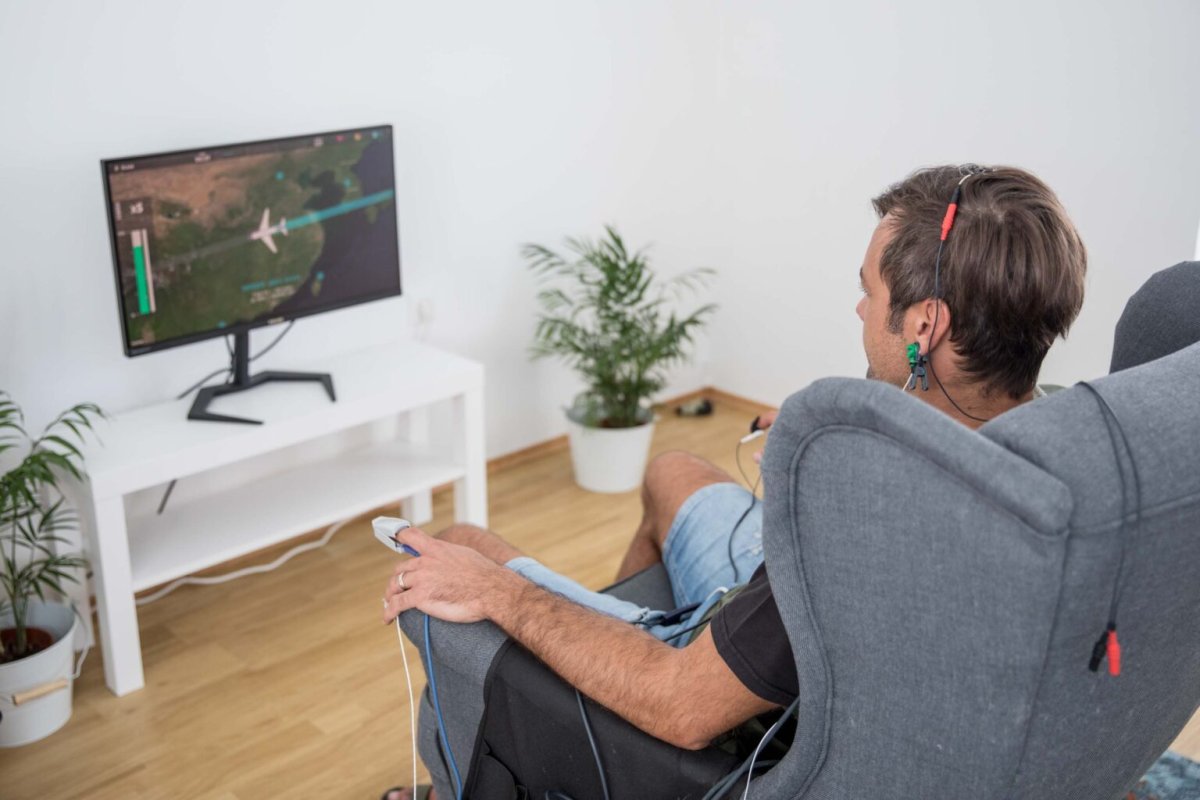

02
The individual is presented with games on the screen that aim to provide feedback about brain activity and mental states. The content is designed to clearly and simply indicate whether the person is in a desirable or undesirable mental state. When the current mental state is favorable, the person receives positive reinforcement from the game in the form of attractive images, pleasant music and sounds, as well as success and progress within the game. Video content and music can also be used during training for feedback purposes. When the current mental state is unfavorable, the individual receives negative reinforcement: the game activity stops, and unpleasant sounds are played. This way, the brain learns new activity patterns that are more beneficial for the individual's functioning, optimizing cognitive and emotional processes.
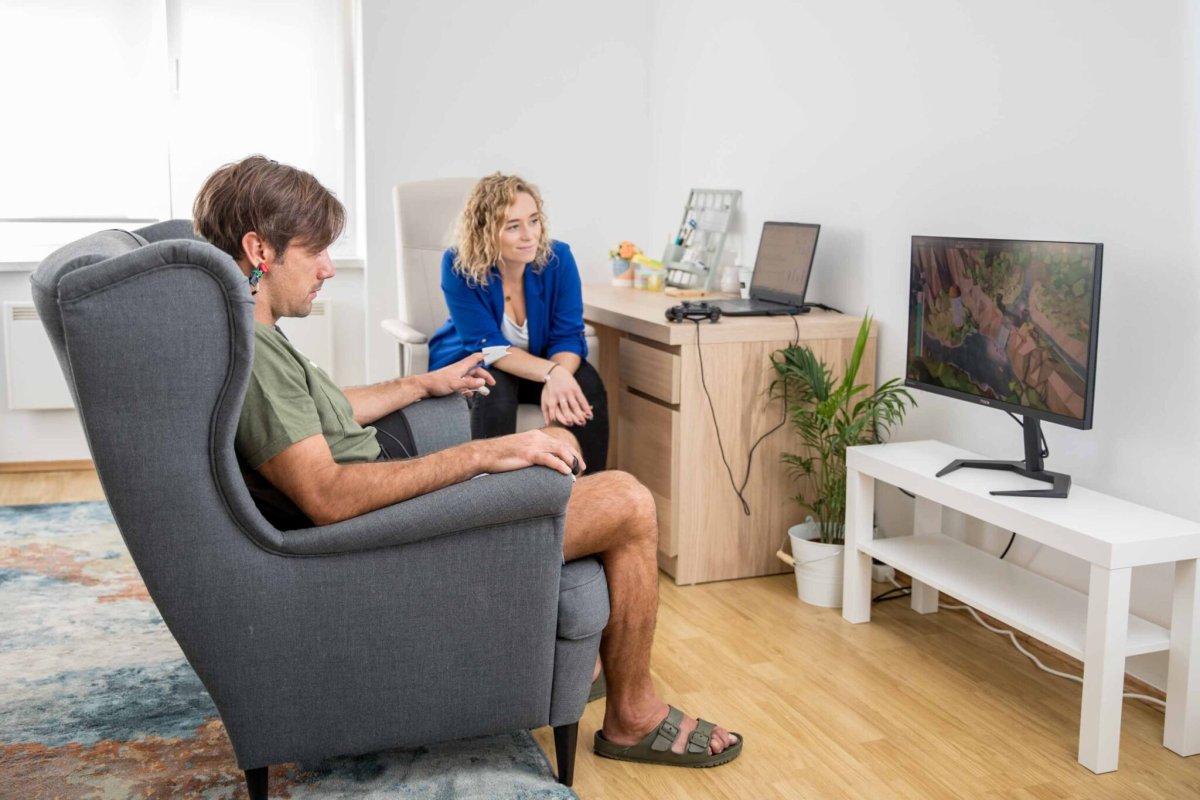

03
Throughout the training session, a therapist is by your side, adjusting the training settings according to your individual needs at that moment. After each game, you discuss with the therapist how well you performed, whether you were able to recognize undesirable states when negative feedback was given, and the therapist provides feedback on the biological parameters we measure.
APPLICATION OF NEUROFEEDBACK
Today, we know that neurofeedback can be applied to a wide range of issues faced by both children and adults. Modern research in neurofeedback also focuses on gathering information about its effectiveness in enhancing performance among professional athletes, managers, and top musicians. Therefore, one of our key focuses is working with individuals who want to improve themselves and their functioning, maximizing their potential. Neurofeedback is applied in cases of ADHD, attention and focus difficulties, depression, anxiety, obsessive-compulsive disorder, panic attacks, PTSD, tics, Tourette syndrome, sleep disorders, dementia, epilepsy, tinnitus, traumatic brain injuries, aphasia, and many other challenges.
FREQUENCY AND DURATION
Neurofeedback sessions are typically conducted twice a week for 45 minutes. However, more frequent sessions can be arranged for performance enhancement. In most training sessions, we also combine biofeedback methods to ensure that the results positively affect the overall body and its regulation. When it comes to performance improvement, 20 sessions are generally sufficient for most adults. On the other hand, if an individual is addressing specific issues, approximately 30 sessions are usually needed.
Assessment
Before starting neurofeedback training, we conduct an initial assessment aimed at determining baseline electrophysiological measures, developing a training plan, setting expected goals, identifying realistic objectives, and deciding how and at what pace the sessions will be conducted.
The assessment includes an interview with the therapist, a questionnaire about daily functioning, and the recording of baseline electrophysiological measures, which may also incorporate other types of biofeedback methods. At the end of the assessment, the therapist reviews the results with you to ensure you understand what will be worked on and how.
NaruÄŤi se
Evaluation
Completion of trainingAt the end of the training, your trainer will analyze and provide feedback on how the session went. We record and track each of your results to ensure continuous progress and to help you understand your current performance level, as we believe that every piece of feedback is important.
After 20 training sessions, we conduct an evaluation recording that includes measuring baseline electrophysiological metrics, just like in the initial assessment. Based on this recording, we gain insight into the results achieved, allowing us to determine whether additional training is necessary and to what extent. We repeat the same process after the training is completed, and in both cases, you will receive a written report.
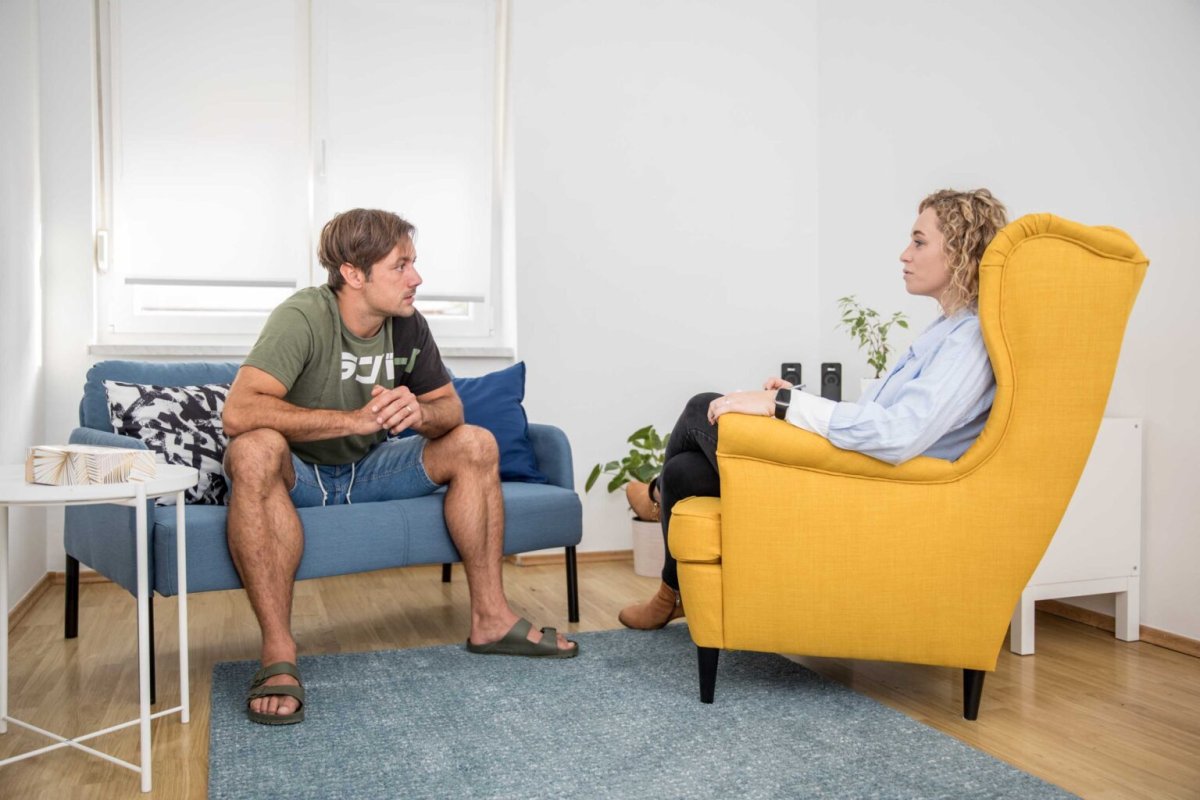

Counseling
Since training sessions at Brainwork are conducted by psychologists, each meeting includes counseling. However, after 15 training sessions, we schedule a meeting that focuses solely on counseling rather than training. This session is dedicated to analyzing your progress in terms of behaviors, changes you notice in yourself, and those observed by the trainers. Together, we fill out a questionnaire similar to the one used in the initial assessment to gather as much relevant information as possible to facilitate further progress. During this session, we discuss both the positive and negative phases you are experiencing, sharing positive experiences as well as any challenges you may face. In short, it is a session focused on psychological counseling. Additionally, based on your needs and preferences, we can arrange counseling with our partners.

